[{“部分”:“新闻”,“文本”:“2023年迪拜国际皮革展|服务全球皮革和时尚行业|现在注册”,“LandingURL”:“https://adsclick.fibre2fashion.com/app/clk/?q=07lrR3Iex48lWl + gszBH7x8K0JeON8Mq3yrDChrjVeCIoJ2O4CfXkfu5xC5ZdJ8ko8e7UpuSahzjDcuMbXOk5McSqLNLpE4pBe0klcKjisScAr + SosTy157ROAeW + P0qDbIkx7kkEyZaEjwc3sgj8mcZ88KHw6/1LK1EsIoQ8suBLP4fi / tVWEvn5TmrvZ4b7OjuE9 + Xj4DifS6Hb5XAp9W49W9GSB6h0bbL6Yze + ijfXxMbmk / kzmGH1MeqyJz + 8 yourmpauofe8snm8uzx7fbow + IkR + F7u + S2LgaHfUCF3Sk6vX2vUkFADuRnZZ6DTp8T0KHx18gF4C0g2tJz0D7vhJzlpijeUN37y49kCGXnRQ3pHXDY / rmH2fRWed5kwJLgqwzTxpzyqd3dw9NVExYtw7Ldhk0A1j j5id + KZNxKwJFF7Ey8xgdO7kcFxHWn9etFCgdW5z0uae9LespmTbg70n0BUWfH4Vw5SE2qsc3jemnLf2iFFs4a+GZkcAodOOZaiEA4Guib+wGQ1eX3yayq2zmfDDaB94ENalJE8uCweMirg7rmMALfme+GrtQ", "Order": "1", "Type": null, "ImpressionURL": "https://static.fibre2fashion.com/spacer.gif"}]
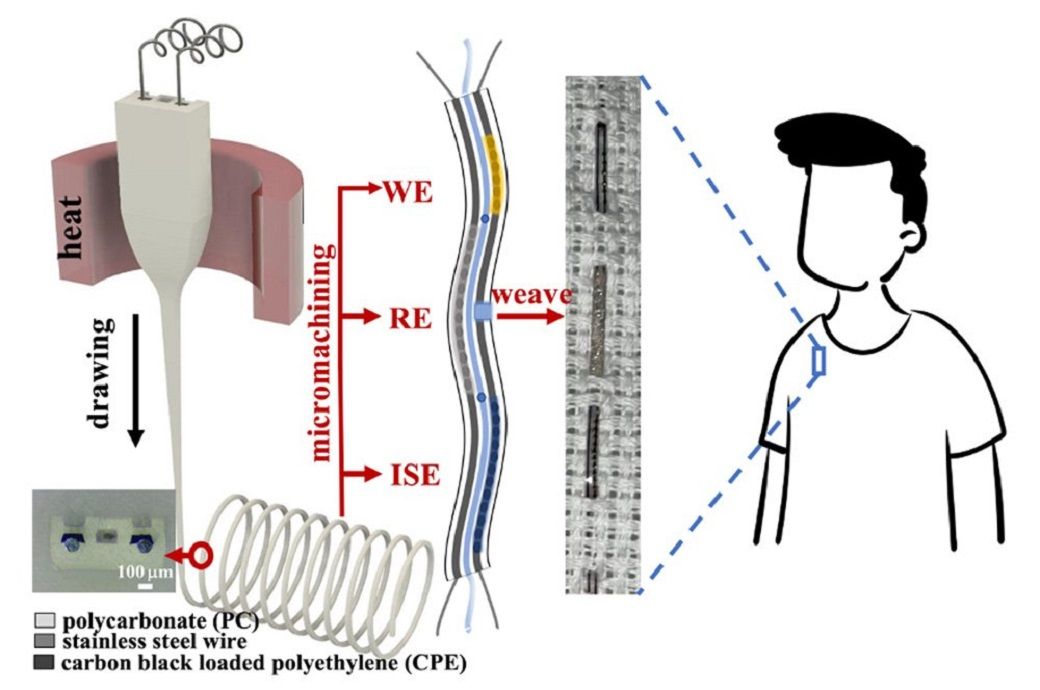
日本东北大学跨学科科学前沿研究所的助理教授郭园圆博士领导的研究小组开发了一种微电子纤维能够分析汗液中电解质和代谢物的显微参数。这种纤维的微米级使得它可以被编织成用于医疗保健的衣服。这种纤维可能会导致基于纤维的智能服装,在功能上提供更大的通用性,更大的传感区域和更高的舒适度。据日本东北大学的一份新闻稿称,该团队认为,他们开发的智能织物可以彻底改变纺织和医疗行业,造福整个人类社会。日本东北大学跨学科科学前沿研究所郭媛圆博士领导的研究团队开发了一种具有微观参数的微电子纤维,能够分析汗液中的电解质和代谢物。这种微米级的纤维可以织进衣服里,用于医疗保健。为了生产这种纤维,该小组利用了通用的热拉伸工艺,在这种工艺中,加热从宏观预制体中抽出微结构纤维。 The team also patterned on two sensing electrodes for sodium and uric acid on the longitudinal surface of the fibre.Although mainstream photolithography and printing technology have enabled wearable electronics, doing so often entails attaching fairly rigid electronic patches to existing fabrics or directly on the skin, leading to only a small area of the body being covered.
Smart fabrics allow for the seamless integration of electronics, optics, biosensors, and mechanics into a thin strand of fibre that is intrinsically flexible and as thin as a human hair. These fabrics can then be used to monitor vital physiological signals related to our mental and physical health status.
Guo said: “Our breakthrough is the first successful attempt at using thermally drawn fibre in wearable bioelectronics for monitoring biochemical signatures.
"Since most developments so far could not be considered clothes, we devoted our effort to transforming fibre, to make truly wearable smart fabric.”
Graduate student Jingxuan Wu was the leading author of the research work, and it was published in Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry on January 9, 2023.
Fibre2Fashion News Desk (DP)